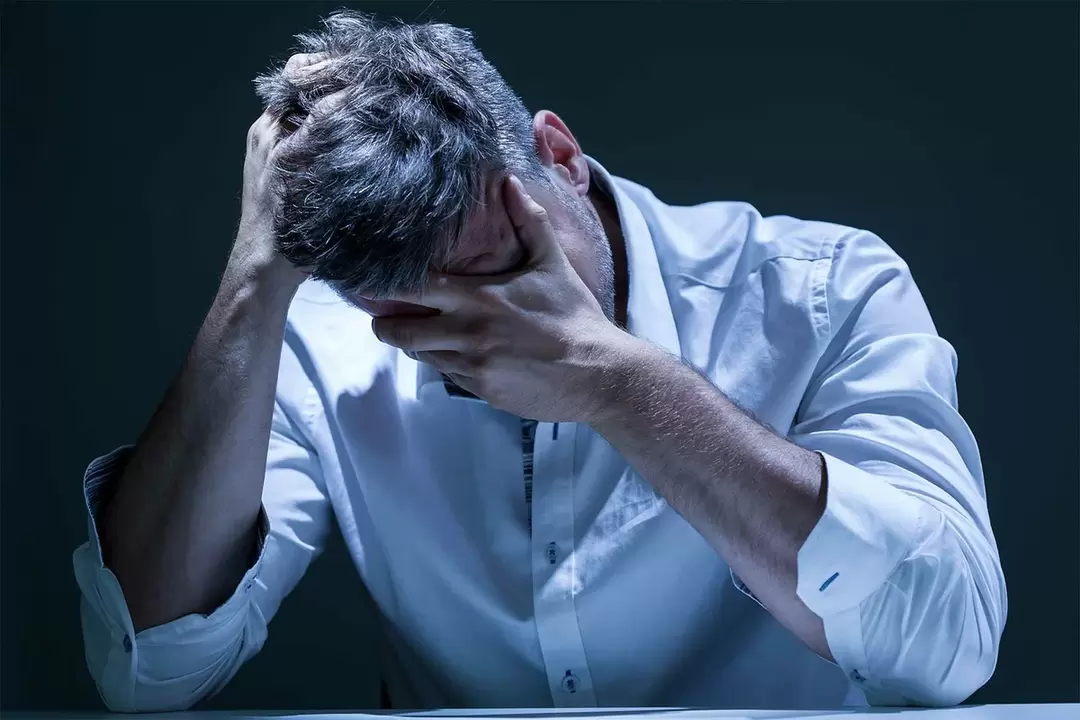
The term "prostatitis" refers to a chronic or acute inflammatory process of any etiology that occurs in the prostate. Since the prostate is an organ unique to men, prostatitis occurs only in men. There are many types of prostatitis, but any kind of prostatitis can be divided into acute and chronic.
Acute prostatitis occurs under the influence of many factors - the influence of bacteria, viruses, the presence of protozoa, malnutrition, a sedentary lifestyle, bad habits, etc. >
The prostate is an exocrine gland, ie it produces secrets into the external environment. In humans, the prostate is an unpaired organ whose activity depends on androgens, especially androgens and steroid hormones.
The prostate sits behind the bladder and grips the initial portion of the urethra into which its catheter passes.
It is because of its location that the prostate performs one of its functions - during an erection, it blocks the outlet of the bladder. It is the prostate that is responsible for the sensation of orgasm, which is due to the gland's rich supply of nerves, i. e. innervation.
temperature
Regardless of the cause, one of the first signs of acute prostatitis is an elevated body temperature. As with any other inflammatory process taking place in the body, the temperature rises to a low calorific value - i. e. around 37. 5-380from.
And, the stronger the immune response, the body's response, the higher the temperature rise. That is to say, when the disease is the most serious, the body temperature can rise to forty degrees.
Of course, only elevated body temperature does not explain the occurrence of prostatitis.
Often, the first symptom of prostatitis is difficulty urinating using extra muscles - abdominal muscles, violation of the ejaculation mechanism, itching, burning and other uncomfortable phenomena in the perineum or genitals.
frequent toilet visits
Additionally, it's an increased urge to urinate (release of small amounts of urine), a "residual urine" feeling after emptying the bladder, unpleasant orgasms, and decreased libido as a result.
general weakness
As with any other inflammatory disease, there is a toxic syndrome including general weakness, decreased performance, nausea and possibly vomiting.
There is also a neurological disorder - depression, irritability, etc.
what causes prostatitis
There are also factors that trigger prostatitis - hormonal imbalance, including age, chronic sexual abstinence, smoking, general hypothermia, fecal retention, sedentary lifestyle, physical inactivity, overheating, chronic sciatica, immunodeficiencyState, age related body.
Predisposing factors such as inflammatory disease of the kidneys and urinary tract deserve special attention because infections can spread upward.
The disease begins with urethritis
The initial stages of prostatitis have fairly typical clinical manifestations - drowsiness with urinary flow, frequent urination, fever. Perineal pain may be possible. Sexual functioning is often violated.
Sexual dysfunction, however, is more of a psychological aspect, physical or clinical. The ejaculation process itself is either not pleasurable at all, or it can even cause pain, creating a conditioned reflex that can lead to decreased libido.
Purely physiologically, prostatitis can only lead to a lack of potency at an advanced stage. The initial stage is also called the "first sign" stage - the onset of urination will not happen immediately as usual, but there will be a slight delay.
At this stage, the prostate has enlarged but is painless to palpation. At the same time, the margins of the prostate were well palpated and the median sulcus was palpated - as normal. Most interestingly, the phase of the first signs can last quite a long time - up to three years.
In recent years, the patients of urologists are getting younger and younger. That is, inflammation of the prostate "gets younger". This is due to the development of "outrageous" recreational activities - surfing, diving, skiing and kayaking. Prostatitis may occur due to insufficient load and complete hypothermia of the body.
And, paradoxically, an overly "calm" lifestyle can also lead to the development of prostatitis. This is due to the stagnation of blood and lymph in the pelvis - a sedentary lifestyle is not the best way to distribute blood in the organs.
Inflammatory diseases that have not been fully cured may have nothing to do with pelvic organs at all, and are also factors that induce prostatitis. This is because infection (of any etiology) from the primary tumor can penetrate the prostate through hematogenous or lymphatic origin. In the presence of pelvic congestion, the infection settles there and begins to multiply.
Prostatitis can also occur due to stress. Stress weakens the immune system, which increases the risk of prostatitis.
STDs - "sexually transmitted diseases" - one of the main causes of prostate inflammation. Gonorrhea, if not treated properly, almost always causes prostatitis.
However, don't forget that one cannot go from one extreme to the other. With prolonged sexual abstinence, blood and lymph fluids in the pelvic organs form stagnation again, a secret stagnation in the prostate, which leads to prostatitis.
The prognosis for prompt detection and adequate treatment of this disease is favorable, however, if the disease is incidental, chronic or increased secondary infection is possible, with rather tragic consequences.