- Prostate abscess;
- Cystitis.
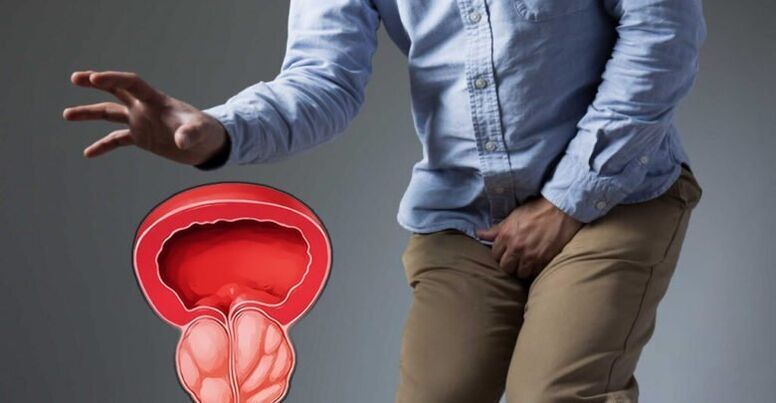
Prostatitis or prostate adenoma?
Causes of prostatitis
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- Enterococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- Chronic infectious diseases (tonsillitis, sinusitis, etc. );
- Other opportunistic pathogens.
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Sedentary work;
- long-term abstinence;
- excessive sexual activity;
- Intercourse interrupted.
- chronic constipation;
- low temperature;
- Unbalanced diet;
- urinary tract disorders;
- often under stress;
- Poisoning of the body due to smoking or drinking;
- Perineal injury.
Types and symptoms of prostatitis
- Catarrhal (painful frequent urination, sacral and perineal pain, difficulty with defecation);
- Follicles (the pain intensifies and begins to radiate to the anus, a thin stream of urine flows out when going to the toilet, and the body temperature rises to 37. 5°C);
- Parenchyma (body temperature rises to 38–40 ° C, systemic intoxication is observed, severe throbbing pain in the groin area, acute urinary retention occurs).
- Weakened erection;
- accelerated ejaculation;
- The severity of sexual feelings decreases.
In some cases, chronic prostatitis becomes the result of an acute process when the patient notices so-called false improvement and refuses to see a urologist. Often, self-medication at home can lead to many complications: abscesses or prostate adenomas, bladder inflammation, loss of fertility, etc.
- herpes,
- bacteria,
- contagious,
- fungi,
- suppuration,
- Chlamydia,
- gonorrhea,
- Good at calculation,
- fibrous,
- Stagnant.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
- General blood and urinalysis;
- Biochemical blood tests are performed to clarify the condition of the disease and determine the involvement of other internal organs and systems in the inflammatory process;
- PSA blood test;
- Urine culture and antibiotic susceptibility testing.
- Genitourinary tract infection smear to detect STDs.
Treatment of prostatitis
Treatment of acute prostatitis
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
Prevent prostatitis
Questions and Answers
- Rapid increase in body temperature (up to 40 degrees);
- severe headache;
- A fever begins.
Urination is impaired and purulent discharge begins in the anus and urethra. Chronic prostatitis can also lead to erectile dysfunction. Ejaculation becomes painful and sexual intercourse becomes unpleasant.
- Seminal vesiculitis. This disease is characterized by an inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles. As a result, pus enters the semen and sperm quality decreases. Seminal vesiculitis often results in complete loss of reproductive function.
- Qiuyan. Diseases in which the inflammatory process affects the spermatozoa. As a result, men experience severe pain during sexual intercourse, leading to an interrupted orgasm. Without treatment, a man can develop psychogenic impotence.
- abscess. It forms in the prostate and causes poisoning in the body. Its rupture can lead to worsening symptoms and, in some cases, death.
- Infertility. It occurs against the background of deterioration of sperm quality and inflammatory processes in the testicles, spermatic cord and vesicles.
- Against the background of prostatitis, immunity often decreases. About one-third of all cases of the disease that go untreated eventually develop tumors. Prostatitis must be treated in specialized men's clinics.
- General blood and urine tests;
- STD smear test;
- secret research;
- Uroflowmetry;
- Ultrasonography.